Understanding the Design and Components of Medical Syringes
Introduction
Syringes are essential tools in modern medicine, widely used for administering medications, vaccines, and drawing fluids. Knowledge of the different components of a syringe is crucial for healthcare professionals, ensuring accurate dosing, safe usage, and proper handling. A clear understanding of each component enhances both patient safety and efficiency in clinical procedures.
Main Components of a Syringe
A syringe comprises several critical parts, each serving a specific function. Understanding these through a visual or descriptive representation is key for effective use.
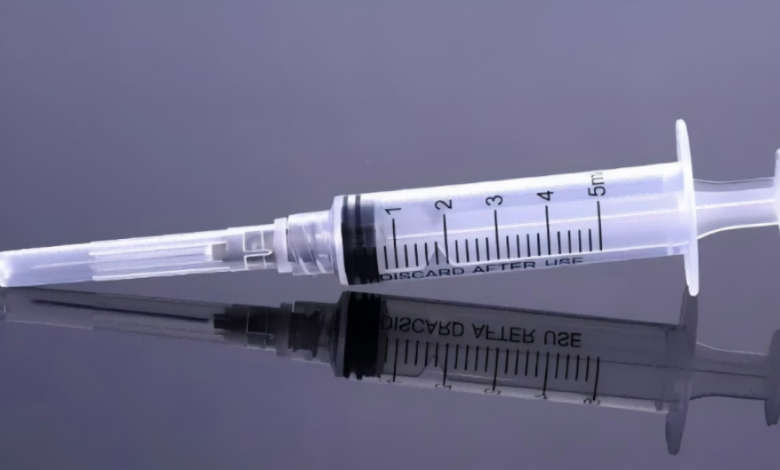
Barrel
The barrel is the cylindrical portion that holds the liquid to be injected or withdrawn. It is typically transparent or semi-transparent, allowing users to monitor the contents. Markings on the barrel indicate precise volumes, which are essential for accurate dosing.
Plunger
The plunger fits snugly inside the barrel and moves back and forth to draw or expel fluid. The tip of the plunger has a rubber or silicone seal to prevent leaks. Smooth movement of the plunger ensures precise administration and minimizes the risk of air bubbles entering the liquid.
Needle
The needle is the pointed metal component that penetrates the skin or container. Needle length, gauge, and bevel type are important factors to consider, as they affect the ease of injection and patient comfort. The needle attaches securely to the syringe via the tip connection.
Tip Connection
The tip connects the barrel to the needle. Common designs include Luer lock tips, which secure the needle by twisting, and slip tips, which allow the needle to be pushed on and removed easily. The type of tip impacts safety and ease of use.
Safety Features
Some modern syringes include safety features like retractable needles or protective caps. These components reduce the risk of accidental needlestick injuries and contamination.
Types of Syringes
Syringes vary in design depending on their intended application.
Standard Syringes
These are general-purpose syringes used in hospitals parts of a syringe and clinics. They consist of a standard barrel, plunger, and needle. Understanding the parts of a syringe in this type is essential for proper administration of medications.
Insulin Syringes
Insulin syringes are designed for subcutaneous injections. They have smaller barrels and fine-gauge needles. Recognizing the components ensures precise dosing for diabetic patients.
Prefilled Syringes
Prefilled syringes come with the medication already loaded in the barrel. They are convenient, reduce preparation time, and minimize contamination risk. The plunger and tip connection are designed for safety and ease of use.
Tuberculin Syringes
Used for specific small-volume injections, these syringes have a narrow barrel and precise markings. Familiarity with the parts of a syringe in this design ensures accurate delivery of small doses.
See also: Unlocking the Power of Hydrogen for Health and Wellness
Importance of Knowing Syringe Components
Knowledge of the parts of a syringe is vital in multiple healthcare scenarios:
Accurate Medication Administration
Understanding the barrel markings, plunger function, and needle specifications helps healthcare providers deliver the correct dosage. This minimizes errors and improves treatment outcomes.
Vaccine Delivery
Vaccines require precise injection. Knowing the components of a syringe ensures proper needle selection, accurate measurement, and safe administration.
Laboratory Applications
In laboratories, syringes are used for sample collection and fluid transfer. Awareness of each part ensures correct usage and reduces contamination risks.
Patient Safety
Recognizing the parts of a syringe promotes safe handling. Healthcare providers can prevent accidental needlestick injuries and ensure sterility by using syringes correctly.
Maintenance and Safety Practices
Proper maintenance and safety measures are essential when handling syringes.
- Always use a sterile syringe for injections or sample collection.
- Inspect the barrel, plunger, and tip connection for defects before use.
- Avoid recapping needles to reduce injury risk.
- Dispose of used syringes in approved sharps containers.
These practices, supported by an understanding of syringe components, enhance safety for both patients and healthcare workers.
Innovations in Syringe Design
Modern syringes often incorporate advanced features that improve safety and efficiency.
- Safety syringes: Retractable needles prevent needlestick injuries.
- Ergonomic designs: Enhanced grips and smooth plunger operation reduce user fatigue.
- Prefilled syringes: Reduce preparation errors and contamination risk.
Being familiar with these components allows healthcare professionals to select the most appropriate syringe for a given situation.
Training and Education
Visual aids, diagrams, and detailed descriptions of the parts of a syringe are invaluable in medical education. They help:
- Train healthcare workers without direct patient contact.
- Demonstrate correct injection techniques.
- Reduce errors in fluid measurement and needle handling.
Incorporating these tools into training programs improves competency and confidence in clinical practice.
Conclusion
Understanding the parts of a syringe is fundamental for anyone in healthcare. From the barrel and plunger to the needle and tip connection, each component plays a critical role in safe and effective medication administration. Proper knowledge, combined with safe handling practices, ensures accurate dosing, minimizes contamination risk, and protects both patients and healthcare workers. Whether in hospitals, clinics, or laboratories, a thorough comprehension of syringe components enhances efficiency and patient care.



